Why Material Selection Matters in High-Fidelity Audio Manufacturing
High-fidelity (hi-fi) audio manufacturing is as much an art as a science when it comes to achieving the optimum balance between sound quality, lifespan, and looks. Be it audiophile-grade headphones, studio monitors, or groundbreaking smart speakers, materials in audio production are a significant consideration in determining the final sound signature.
From driver membranes to enclosures and damping materials, every component has a role to play in the way audio waves interact, resonate, and ultimately find their way to the listener’s ears. In this piece, we explore the science of materials selection and why top audio brands pay such close attention to it.
The Science of Sound: Why Materials Matter
Before we get into material specifics, let’s understand why they matter. Every material carries its own set of characteristics that affect sound transmission, resonance, and damping. Materials affect:
- Frequency Response
A device’s capability to recreate different audio frequencies with accuracy. - Resonance Control
Unwanted vibrations that mar audio clarity. - Damping Characteristics
Absorption of excess energy to prevent harshness. - Durability & Weight
A trade-off between ruggedness and portability.
In accordance with the Audio Engineering Society (AES) research, composite material speaker enclosures that are optimised reduce distortion by up to 35% compared to traditional MDF (medium-density fibreboard) cabinets.
Major Materials Used in High-Fidelity Audio Manufacturing
A. Speaker Cone & Driver Materials
The driver is the heart of any audio device, and the material from which its diaphragm is made greatly defines sound reproduction. Common materials include:
- Paper
Lightweight paper cones provide warm, balanced sound but can deteriorate over time. - Polypropylene (PP)
A cheap material with good damping properties, often used in budget and mid-range speakers. - Kevlar & Aramid Fiber
High tensile strength materials that deliver tight, responsive bass and good durability. - Beryllium & Titanium
Very light but rigid metals used in high-end tweeters for accurate high-frequency reproduction. - Graphene
A novel material that’s 200 times as strong as steel but quite lightweight, contributing to responsiveness and detail for the driver.
Beryllium tweeters, as found in high-end brands like Focal and TAD, can extend treble frequencies to 40kHz, beyond human hearing but important in capturing ultrasonic harmonics.
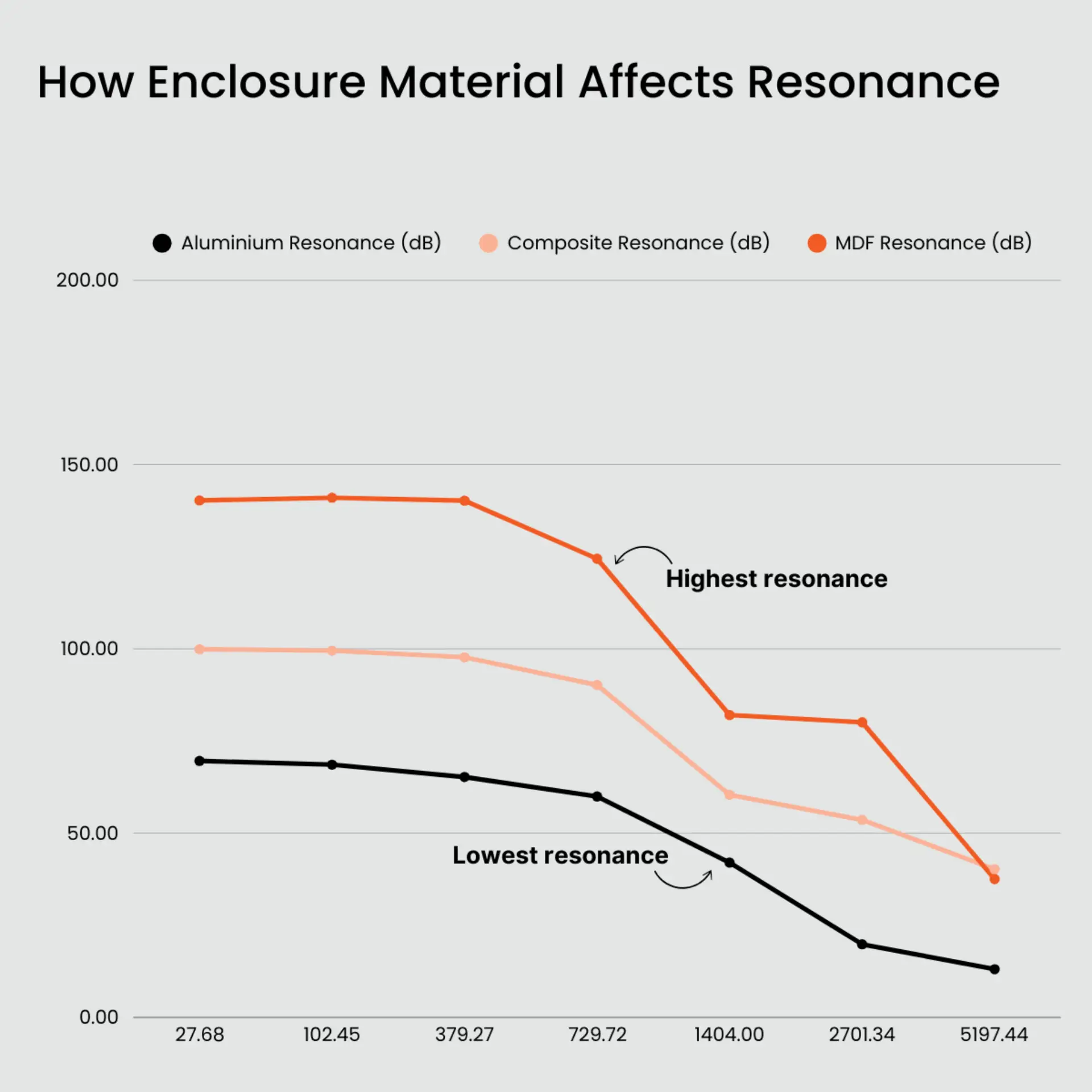
B. Speaker Enclosure Materials
The enclosure plays an important role in preventing unwanted vibration and resonance. Typical enclosure materials include:
- MDF (Medium-Density Fibreboard)
An industry standard for cabinet making due to its density and affordability. - Aluminium
Used in high-end audio products due to its stiffness and heat dissipation. - Wood (Plywood & HDF)
Provides warm and natural resonance, popular in audiophile-grade speakers. - Composite & Carbon FibFibreer
Lightweight and robust, these materials are gaining popularity in portable and pro audio applications.
A study in the Journal of Sound and Vibration concluded that aluminium enclosures reduce cabinet resonance by 60% over MDF, leading to cleaner, more accurate sound reproduction.
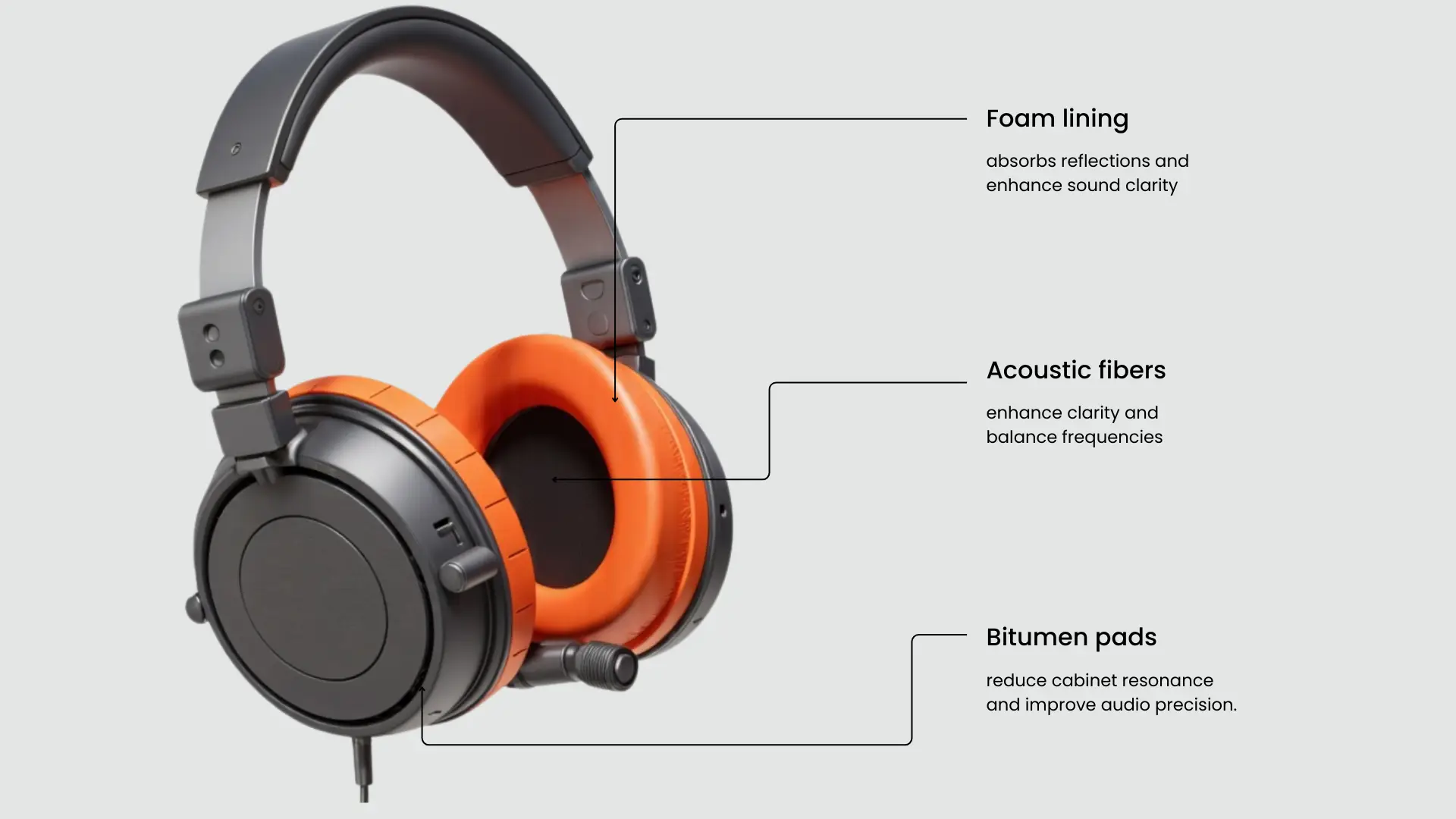
C. Damping & Insulation Materials
Regardless of the quality of drivers and enclosures, there may be unwanted vibrations. Damping materials hold this in line:
- Foam & Rubber
Lining enclosures to disperse stray sound waves. - Bitumen Pads
Employed in high-end speakers to minimize internal reflections. - Acoustic Fibers & Wool
Utilized inside enclosures to prevent standing waves and improve clarity.
The Trade-Offs in Material Selection
During the design of an audio product, manufacturers must compromise between:
- Performance vs. Cost
Exotic materials like graphene and beryllium offer better sound but increase the production cost. - Weight vs. Durability
Protective aluminium enclosures can lead to unwanted bulk. - Production Complexity
Some materials require specialized manufacturing processes, affecting lead time and scalability.
For sourcing companies, awareness of such trade-offs is central to choosing materials that meet acoustic and business goals.
Future Trends in Material Innovation for Audio Devices
The audio industry continues to push the boundaries of material science. Some future trends include:
- Sustainable Materials
Brands like House of Marley are pioneering biodegradable and recycled materials in speakers. - 3D-Printed Audio Components
Advanced additive manufacturing is making custom, lightweight, and highly optimised acoustic designs possible. - Nanomaterials & AI-Optimized Composites
Materials engineered at the molecular level to enhance performance while reducing weight.
Research estimates that by 2030, over 50% of audio brands will incorporate recycled materials into their products to meet increasingly strict environmental laws.
The Power of Smart Material Choices
For audio engineers, product designers, and procurement professionals, materials selection isn’t just a technical decision—it’s a strategic decision. The right material selection can mean the difference between an average product and a revolutionary innovation.
Understanding how materials impact acoustics, production efficiency, and cost will ensure your products deliver the performance, durability, and sustainability that consumers demand today.
So next time you’re designing or sourcing an audio product, remember: sound quality starts with materials.
Explore more related content
Digital Rearview Mirrors: Engineering Challenges & Solutions
Digital Rearview Mirrors: Engineering Challenges & Solutions for Automotive OEMsAutomotive manufacturers are...
The Ultimate Guide to AR, VR, and MR
The Ultimate Guide to AR, VR, and MR: Differences, Popularity, and ChallengesOur world is changing, shaped by the...
Understanding Scope 1, 2, 3 Emissions and how they affect production
Understanding Scope 1, 2, 3 Emissions and how they affect productionIt is essential to understand the differences...
Follow us on
© Intretech Ltd. 2025. All Rights Reserved